P(x 2) 267517-P x^2 commutator
Use the Remainder Theorem to determine whether x = 2 is a zero of f (x) = 3x 7 – x 4 2x 3 – 5x 2 – 4;To find the probability that X is less than or equal to 2, you first need to find the probability of each possible value of X less than 2 In other words, you find the values for P (X = 0), P (X = 1), and P (X = 2)Free web calculator provided by GraphPad Software Calculates the P value from z, t, r, F, or chisquare
Graphing Quadratic Functions
P x^2 commutator
P x^2 commutator-Binomial Probability Calculator Use the Binomial Calculator to compute individual and cumulative binomial probabilities For help in using the calculator, read the FrequentlyAsked Questions or review the Sample Problems To learn more about the binomial distribution, go to Stat Trek's tutorial on the binomial distributionTwo numbers r and s sum up to 5 exactly when the average of the two numbers is \frac{1}{2}*5 = \frac{5}{2} You can also see that the midpoint of r and s corresponds to the axis of symmetry of the parabola represented by the quadratic equation y=x^2BxC


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch2annotated Pdf
P(x) = d(x)q(x) r(x) or p(x) d(x) = q(x) r(x) d(x) where 0 deg(r(x)) < deg(d(x)) Here p(x) is called the dividend, d(x) the divisor, q(x) the quotient, and r(x) the remainder Theorem (Rational Zeros Theorem) Let f(x) = a nx2 a n 1xn 1 a 1x a 0 be a real polynomial with integer coe cients a i (that is a i 2Z) If a rationalThe radius of the sphere is p (see the figure below) Ellipsoids are the graphs of equations of the form ax 2 by 2 cz 2 = p 2, where a, b, and c are all positive In particular, a sphere is a very special ellipsoid for which a, b, and c are all equal Plot the graph of x 2 y 2 z 2 = 4 in your worksheet in Cartesian coordinates ThenAnswer 0221 The binomial table has a series of minitables inside of it, one for each selected
P(a X b), is then represented by the area shown shaded, in Fig 22 The distribution function F ( x ) P ( X x ) is a monotonically increasing function which increases from 0 to 1 and is represented by a curve as in Fig 23Var(X) = E(X2)−E2(X), (2) the second moment minus the square of the first moment We usually denote the variance by σ2 = Var(X) and when necessary (to avoid confusion) include X as a subscript, σ2 X = Var(X) σ = p Var(X) is called the standard deviation of X For any rv X and any number a E(aX) = aE(X), and Var(aX) = a2Var(X) (3)The rational function f(x) = P(x) / Q(x) in lowest terms has an oblique asymptote if the degree of the numerator, P(x), is exactly one greater than the degree of the denominator, Q(x) You can find oblique asymptotes using polynomial division, where the quotient is the equation of the oblique asymptote
Free Algebra Solver and Algebra Calculator showing step by step solutions No Download or Signup Available as a mobile and desktop website as well as native iOS and Android appsNotice the different uses of X and x X is the Random Variable "The sum of the scores on the two dice";Graph p(x)=(x2)(x2)(x3) Find the point at Tap for more steps Replace the variable with in the expression Simplify the result Tap for more steps Simplify each term Tap for more steps Raise to the power of Raise to the power of Multiply by Multiply by Simplify by adding and subtracting Tap for more steps


Question The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y P X Y Is Given By P L 1 0 2 P 1 2 0 0 Studyref
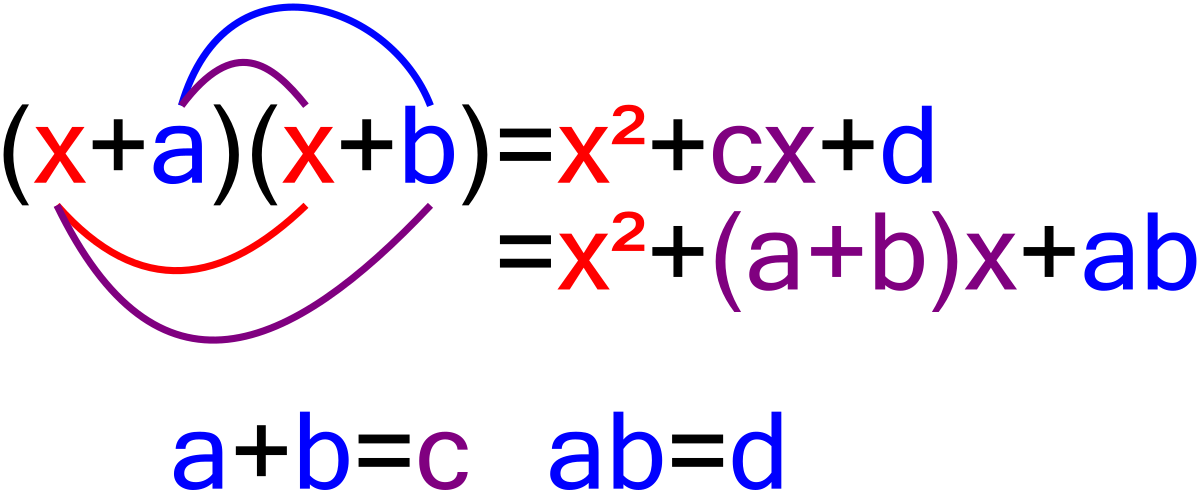


Factorization Wikipedia
Find the latest United States Steel Corporation (X) stock quote, history, news and other vital information to help you with your stock trading and investingCorresponding to P(X ≤ a) P(X ≥ a 1), this area does not sum to 10 because the area from a to (a 1) is missing The usual way to solve this problem is to associate 1/2 of the interval from a to a 1 with each adjacent integer The continuous approximation to the probability P(X ≤ a) would thus beP(a X b), is then represented by the area shown shaded, in Fig 22 The distribution function F ( x ) P ( X x ) is a monotonically increasing function which increases from 0 to 1 and is represented by a curve as in Fig 23


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch2annotated Pdf



If One Root Of The Quadratic Equation 3x2 Px 4 0 Is 2 3 Then Find
The mean is the Sum of (X × P(X)) μ = 36 The variance is the Sum of (X 2 × P(X)) minus Mean 2 Variance σ 2 = 1332 − 36 2 = 036 Standard Deviation is σ = √(036) = 06 And we got the same results as before (yay!)P(a X b), is then represented by the area shown shaded, in Fig 22 The distribution function F ( x ) P ( X x ) is a monotonically increasing function which increases from 0 to 1 and is represented by a curve as in Fig 23Since x is already present in 6x and is a square root of x 2, then 6 must be twice the square root of the number we place in the blank In other words, if we first take half of 6 and then square that result, we will obtain the necessary number for the blank Therefore x 2 6x 9 is a perfect square trinomial Now let's consider how we can use



How To Factorise A Polynomial By Splitting The Middle Term A Plus Topper



Solved Let X Be A Discrete Random Variable Such That P X Chegg Com
P(X < 1) = P(X = 0) P(X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to xXvalue is 0 and whose rightmost xvalue is 1/2 (which is only seen by drawing the figure!) See figure above, right To compute the probability, we double integrate the joint density over this subset of the support set P(Y ≥ X) = Z 1/2 0 Z 1−x x 24xydydx 2Solving the quadratic congruence x 2 ≡ a (mod m) This works for m with up to say digits, due to the limitations of the program used to factor m Using the Chinese remainder theorem, the problem is reduced to the case of a prime power p n
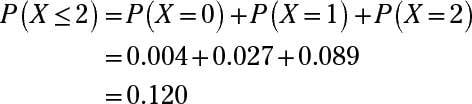


Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies



Ex 2 2 2 Find P 0 P 1 And P 2 For Each Of The Ex 2 2
Corresponding to P(X ≤ a) P(X ≥ a 1), this area does not sum to 10 because the area from a to (a 1) is missing The usual way to solve this problem is to associate 1/2 of the interval from a to a 1 with each adjacent integer The continuous approximation to the probability P(X ≤ a) would thus be6 b When p = 6, 2x 3px (14p − 3) 2= x 2 3(6) x (14(6) − 3) 2 = x 18 x 81 2 2 x 18 x 81 = 0 (x 9)(x 9) = 0 So x = −9 7 a 2h(x) = 2x (k 4)x k a = 2, b = k 4 and c = k 2 b 2− 4 ac = (k 4) − 4 × 2 × k 2 = k 2 8 k 16 − 8 k = k 16 ⩾ b k2 0, therefore k2 16 is also > 0 If b2X is a value that X can take;
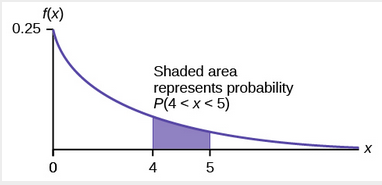


The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics



How Do You Use The Factor Theorem A Plus Topper
The next function we look at is qnorm which is the inverse of pnorm The idea behind qnorm is that you give it a probability, and it returns the number whose cumulative distribution matches the probability For example, if you have a normally distributed random variable with mean zero and standard deviation one, then if you give the function a probability it returns the associated ZscoreY=x^21 Disclaimer This calculator is not perfect Please use at your own risk, and please alert us if something isn't working Thank you How to Use the Calculator Type your algebra problem into the text box For example, enter 3x2=14 into the text box to get a stepbystep explanation of how to solve 3x2=14Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor


Binomial Formula Explained
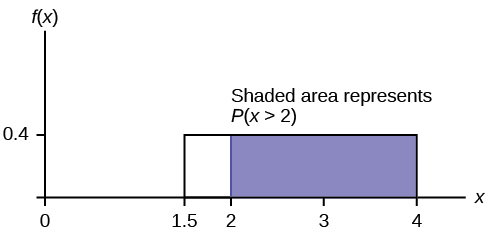


The Uniform Distribution Introduction To Statistics
X In view of (12) and (13) it is natural to define the angular momentum operators by 2p 2 −(r · p) i r · p (138) Another useful and simple identity is the following a · (b× c) = (a × b) · c , (139) as you should confirm in a oneline computation In commuting vector analysis this triple product is known to be cyclicallyGiven f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations context This looks much worse than it is, as long as I'm willing to take the time and be carefulFor x = 2 to be a zero of f (x), then f (2) must evaluate to zero In the context of the Remainder Theorem, this means that my remainder, when dividing by x = 2, must be zero



Solved Find P X Y 1 3 Let The Joint Density Of X And Chegg Com



Completing The Square
Solving the quadratic congruence x 2 ≡ a (mod m) This works for m with up to say digits, due to the limitations of the program used to factor m Using the Chinese remainder theorem, the problem is reduced to the case of a prime power p nFree math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutorGiven f (x) = 3x 2 – x 4, find the simplified form of the following expression, and evaluate at h = 0 This isn't really a functionsoperations question, but something like this often arises in the functionsoperations context This looks much worse than it is, as long as I'm willing to take the time and be careful



Geometric Distribution Wikipedia



Find The Value Of K If X 1 Is A Factor Of P X In The Given Equations Youtube
The company's profit function, P(x) 4 The two points, (x 1, y 1) and (x 2, y 2) at which the company breaks even 5 The output level that maximizes the company's profit, and the maximum profit 1) Revenue is equal to the number of units sold times the price per unit To obtain theThus, the roots of a polynomial P(x) are values of x such that P(x) = 0 The Rational Zeros Theorem The Rational Zeros Theorem states If P(x) is a polynomial with integer coefficients and if is a zero of P(x) (P() = 0), then p is a factor of the constant term of P(x) and q is a factor of the leading coefficient of P(x)P(A) 4/92/9=2/3 2/91/9=1/3 (X) are measured Marginal probability distribution If more than one random variable is defined in a random experiment, it is important to distinguish between the joint probability distribution of X and Y and the probability distribution of each variable individually The individual probability distribution



Ex 2 2 2 Find P 0 P 1 And P 2 For Each Of The Ex 2 2



Variance Wikipedia
See also General Function Explorer where you can graph up to three functions of your choice simultaneously using sliders for independent variables as above See also Linear Explorer and Cubic Explorer This form of a quadratic is useful when graphing because the vertex location is given directly by the values of h and kIn the graph above, click 'zero' under h and k, and note how the vertexVar(X) = E(X2)−E2(X), (2) the second moment minus the square of the first moment We usually denote the variance by σ2 = Var(X) and when necessary (to avoid confusion) include X as a subscript, σ2 X = Var(X) σ = p Var(X) is called the standard deviation of X For any rv X and any number a E(aX) = aE(X), and Var(aX) = a2Var(X) (3)Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with stepbystep explanations
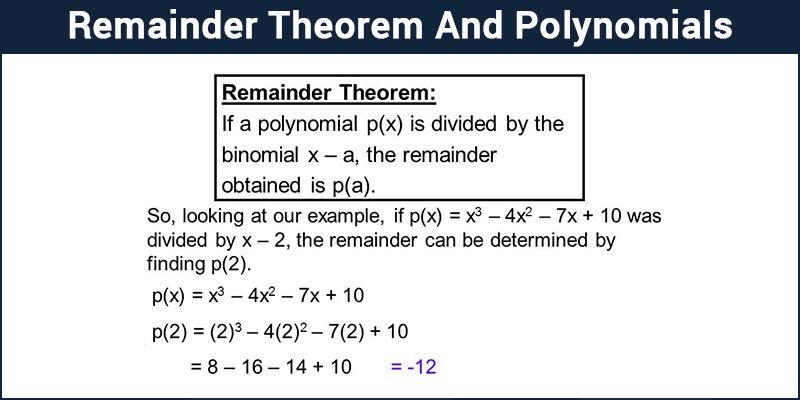


Remainder Theorem Remainder Theorem Of Polynomial Examples



Find The Value Of P For Which One Root Of The Quadratic Equation Px2 14x 8 0 Is 6 Times The Other Mathematics Topperlearning Com Pelbjww
The mean is the Sum of (X × P(X)) μ = 36 The variance is the Sum of (X 2 × P(X)) minus Mean 2 Variance σ 2 = 1332 − 36 2 = 036 Standard Deviation is σ = √(036) = 06 And we got the same results as before (yay!)Continuous Random Variables can be either Discrete or Continuous Discrete Data can only take certain values (such as 1,2,3,4,5) Continuous Data can take any value within a range (such as a person's height)Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor
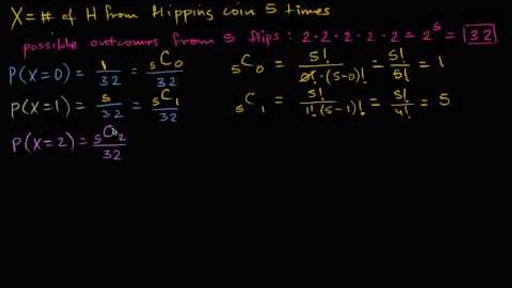


Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy


Graphing Quadratic Functions
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If x 2 = p , where x < 2 , then x p is equal toBasic formulas Any general polynomial of degree n = − − ⋯ (with the coefficients being real or complex numbers and a n ≠ 0) is known by the fundamental theorem of algebra to have n (not necessarily distinct) complex roots r 1, r 2, , r nVieta's formulas relate polynomial's coefficients to signed sums of products of the roots r 1, r 2, , r n as followsThe variance of random variable X is the expected value of squares of difference of X and the expected value μ σ 2 = Var (X ) = E (X μ) 2 From the definition of the variance we can get σ 2 = Var (X ) = E(X 2) μ 2 Variance of continuous random variable For continuous random variable with mean value μ and probability density


Graphing Quadratic Functions


Www Colorado Edu Amath Sites Default Files Attached Files Ch4 Pdf
Examples 1 Suppose the joint pmf of X and Y isgiven byp(1,1) = 05, p(1,2) = 01, p(2,1) = 01, p(2,2) = 03 Find the pmf of X given Y = 1 SolutionP(x)=−2x^228x66 I am going to assume you require us to simplify the function for you P(x)=−2(x−3)(x−11) Expand, P(x)=−2(x^214x33) Expand, P(x)=−2x^228x66Solve calculus and algebra problems online with Cymath math problem solver with steps to show your work Get the Cymath math solving app on your smartphone!



Normal Approximation To The Binomial Statistics How To
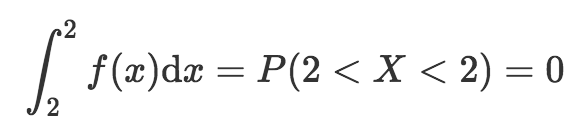


Probability Concepts Explained Probability Distributions Introduction Part 3 By Jonny Brooks Bartlett Towards Data Science
(a) The probability of getting exactly 4 heads out of the six is PX = 4 = f(4) = , the height of the bar at x=4 in the probability distribution graph (the left one) (b) The probability of getting 2 or fewer heads out of the six is P X ≤ 2 = F(2) = , the cumulative value at x =2 in the righthand graph (which equals the sum ofP (x > 2) = 11/16 =6875 Because 2 is the center event and because of the symmetry of a binomial distribution, this probability is the same as P (x < 2) or problem 3F(x) = P(X ≤ x) Continuous distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by integration of the probability density function f(u) of continuous random variable X Discrete distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by summation of the probability mass function P(u) of discrete random variable X
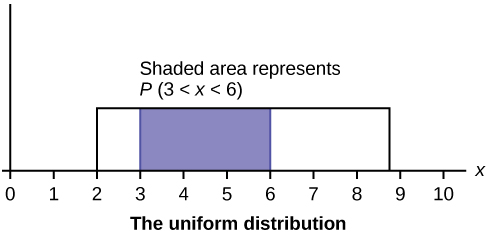


Properties Of Continuous Probability Density Functions Introductory Business Statistics



Ex 2 2 2 Find P 0 P 1 And P 2 For Each Of The Ex 2 2
Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyFor the sample questions here, X is a random variable with a binomial distribution with n = 11 and p = 04 Use the binomial table to answer the following problems Sample questions What is P(X = 5)?


The Binomial Distribution



Probability Density Function Wikipedia



Gamma Distribution Wikipedia



The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics
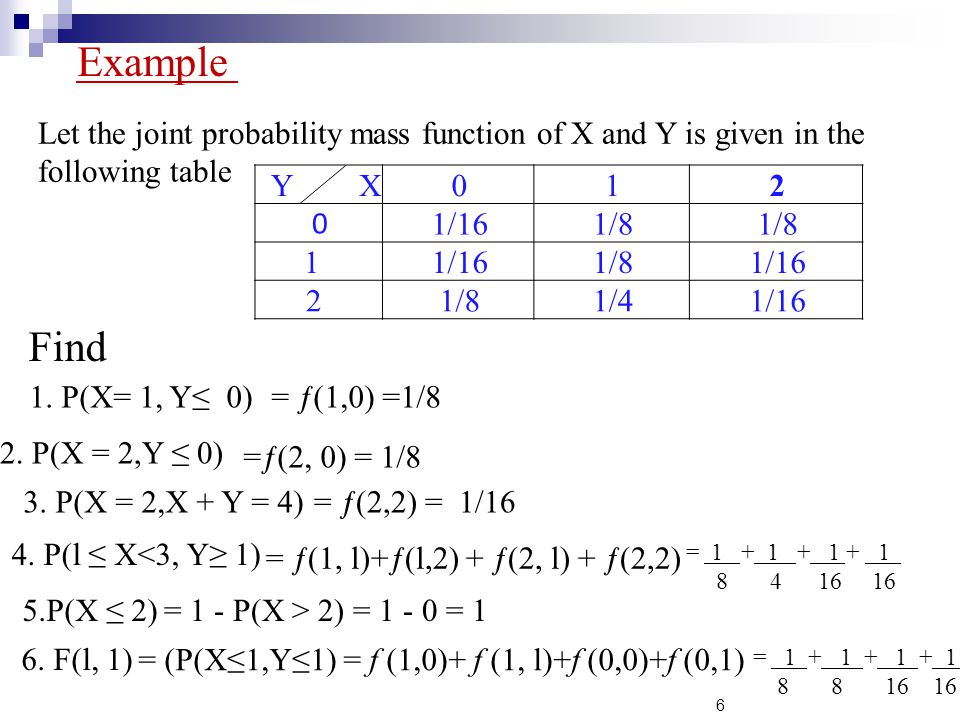


Chapter6 Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download


Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy



Ex 2 2 1 Find Value Of Polynomial 5x 4x2 3 At Ex 2 2


Graphing Quadratic Functions
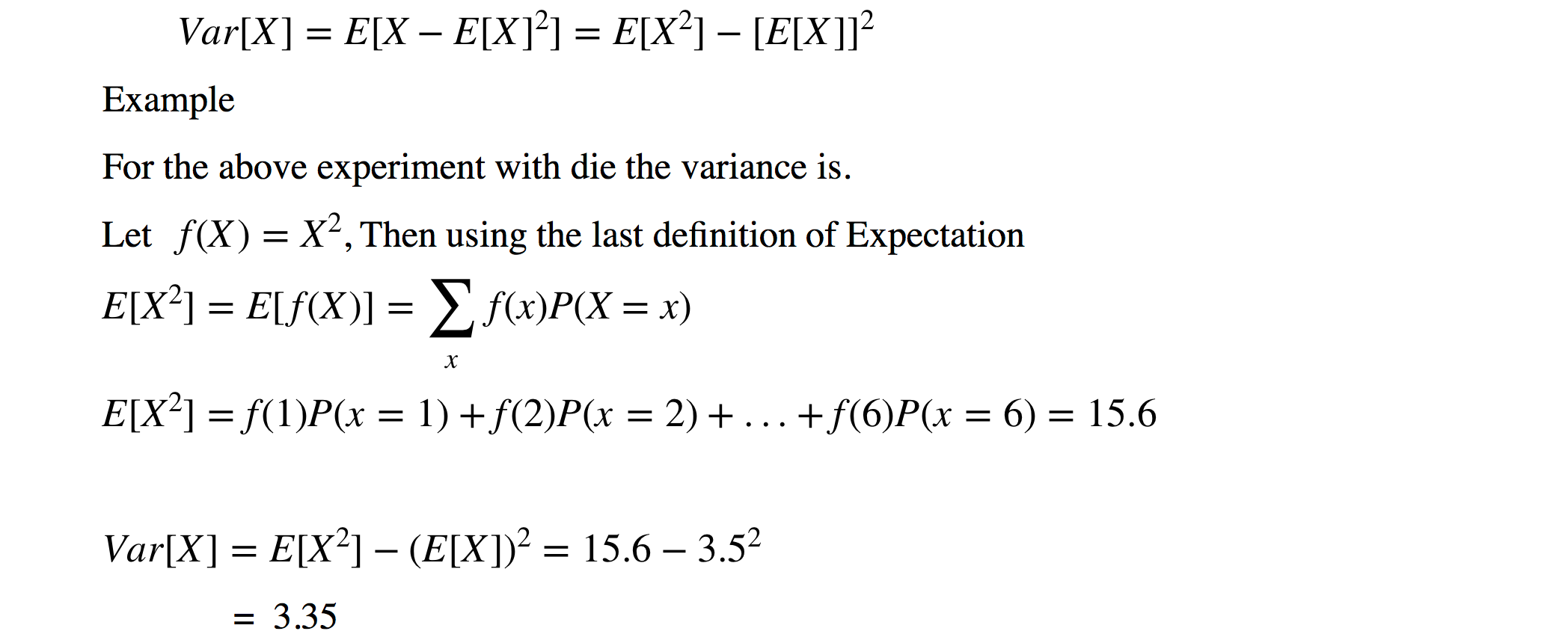


Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science


15 9 The Chi Square Table Stat 414


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch2annotated Pdf


Http Www Columbia Edu Ks 4703 Sigman 4703 07 Notes Arm Pdf



Factor Theorem Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
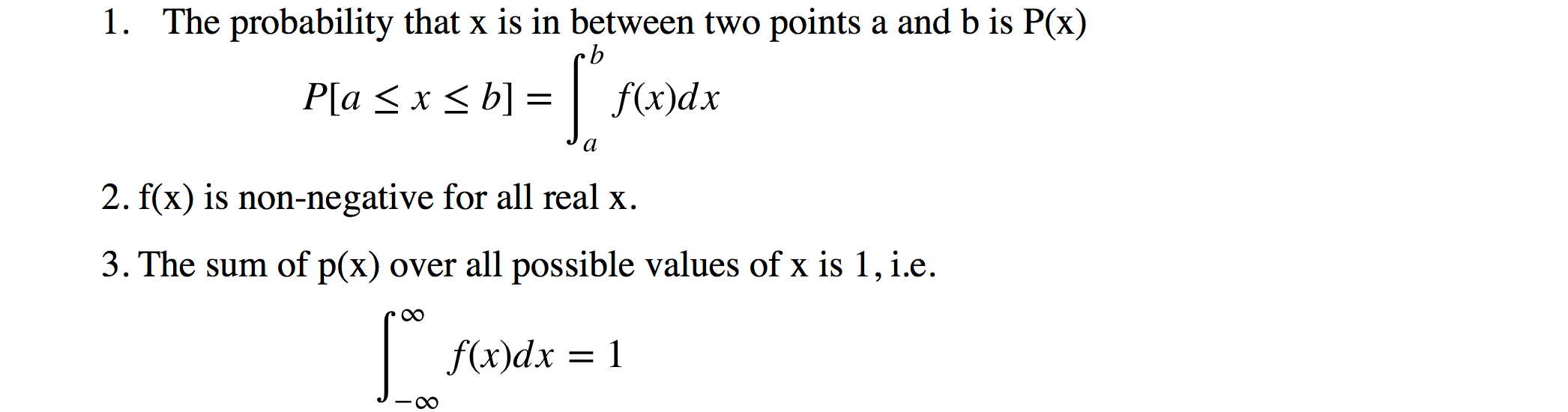


Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science



Solved Why Probability Of Min X Y N Is Same As Probabi Chegg Com



Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science



The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics


P X Y Formula
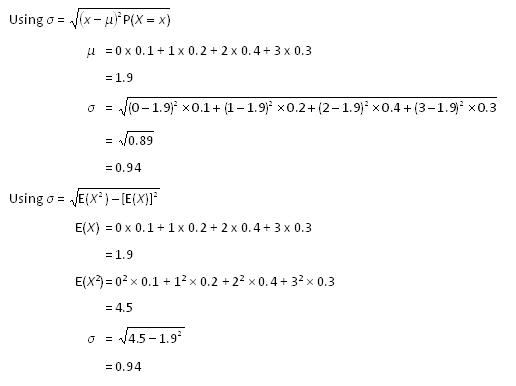


Standard Deviation Of A Discrete Random Variable Nz Maths



Probability With Discrete Random Variable Example Video Khan Academy



Erf From Wolfram Mathworld
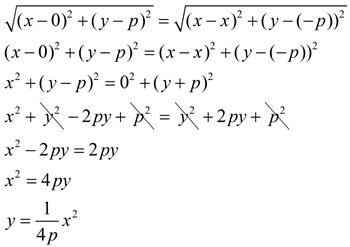


Parabola Equations Mathbitsnotebook Geo Ccss Math



Ex 2 4 3 Find Value Of K If X 1 Is A Factor Of P X



Probability With Discrete Random Variable Example Video Khan Academy



Given That 1 X X 2 N A 0 A 1x A 2x 2 A 2n X 2n Find
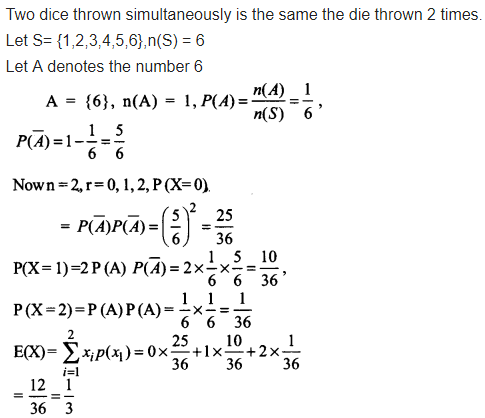


Ncert Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 Probability Ex 13 4



Solved P X 0 0 1 P X 1 0 2 P X 2 0 3 P X 3 Chegg Com
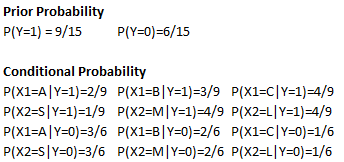


An Introduction To Naive Bayes Classifier By Yang S Towards Data Science



Chapter 2
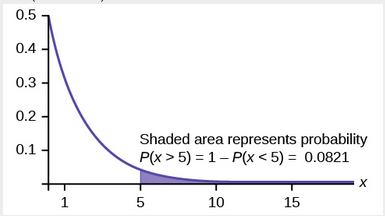


The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics
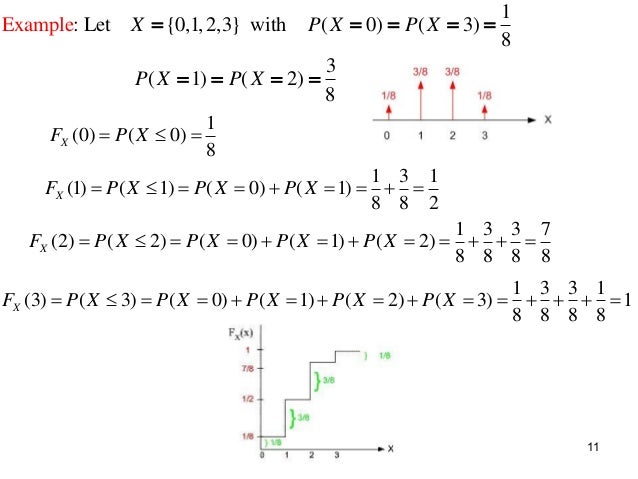


2 Random Variables Notes 2p3



Extracting Square Roots
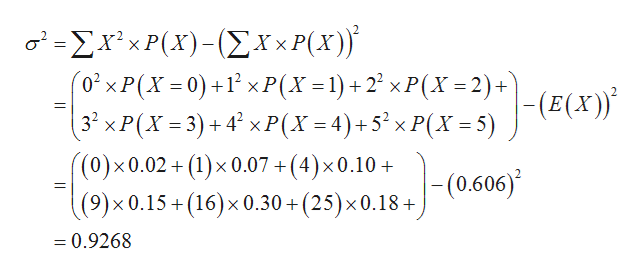


Answered Complete Parts A And B Below The Bartleby



Bayes Theorem Some Perspectives By Garychl Towards Data Science



Ex 2 2 3 Verify Whether Following Are Zeroes Of The Ex 2 2



The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics



Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides



Important Questions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Cbse Tuts



Ex 2 4 3 Find Value Of K If X 1 Is A Factor Of P X
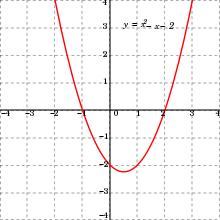


Dependent And Independent Variables Wikipedia
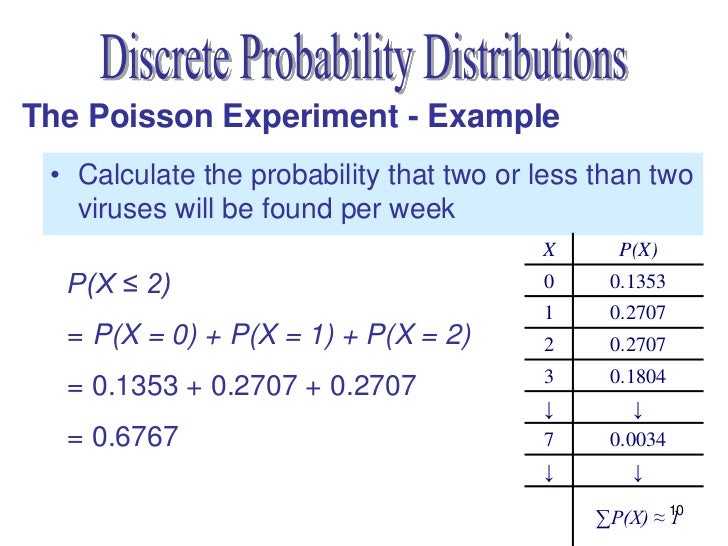


Poisson Lecture


Secure Media Collegeboard Org Digitalservices Pdf Ap Apcentral Ap14 Calculus Ab Q3 Pdf
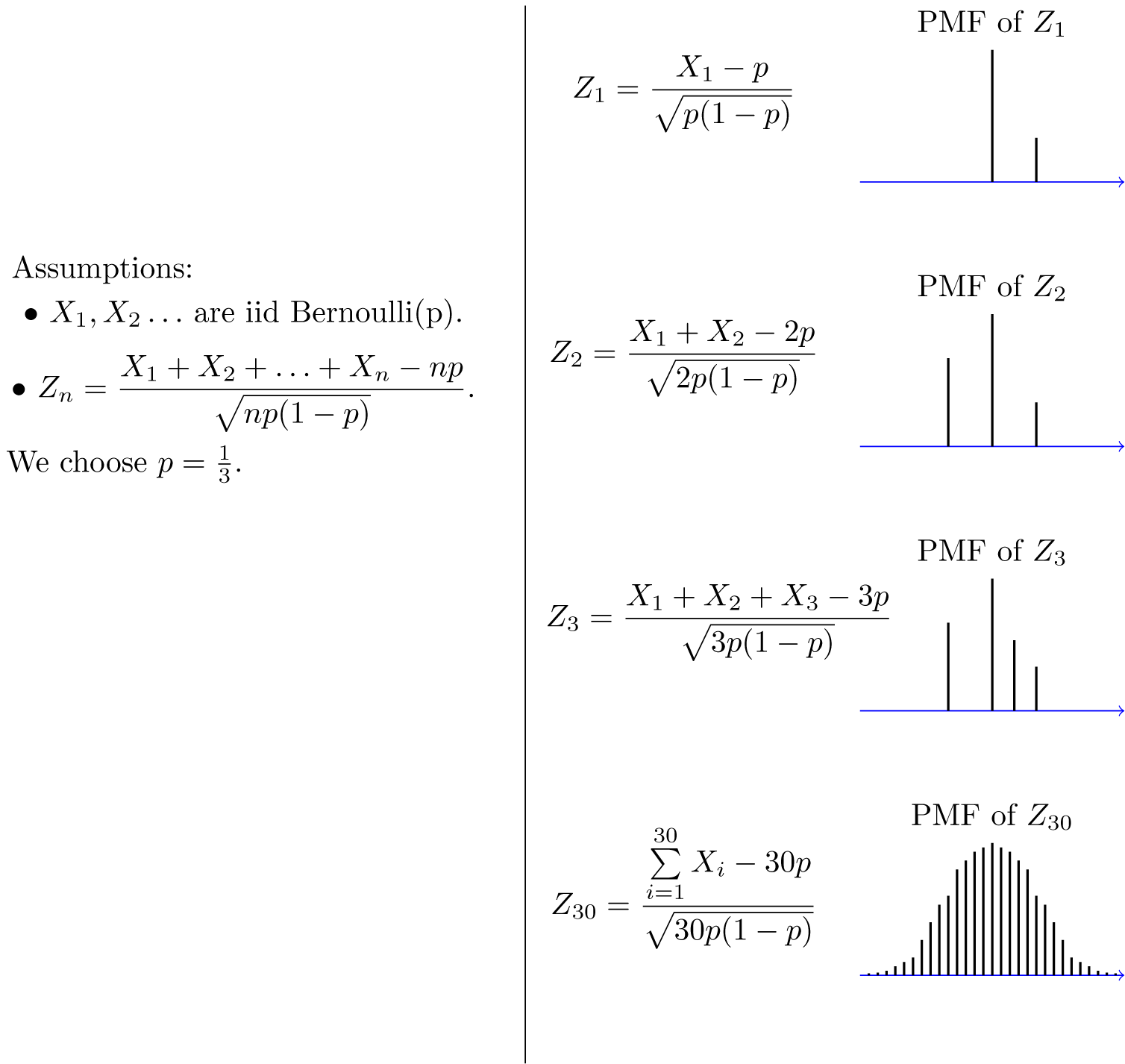


7 1 2 Central Limit Theorem



Geometric Distribution Wikipedia
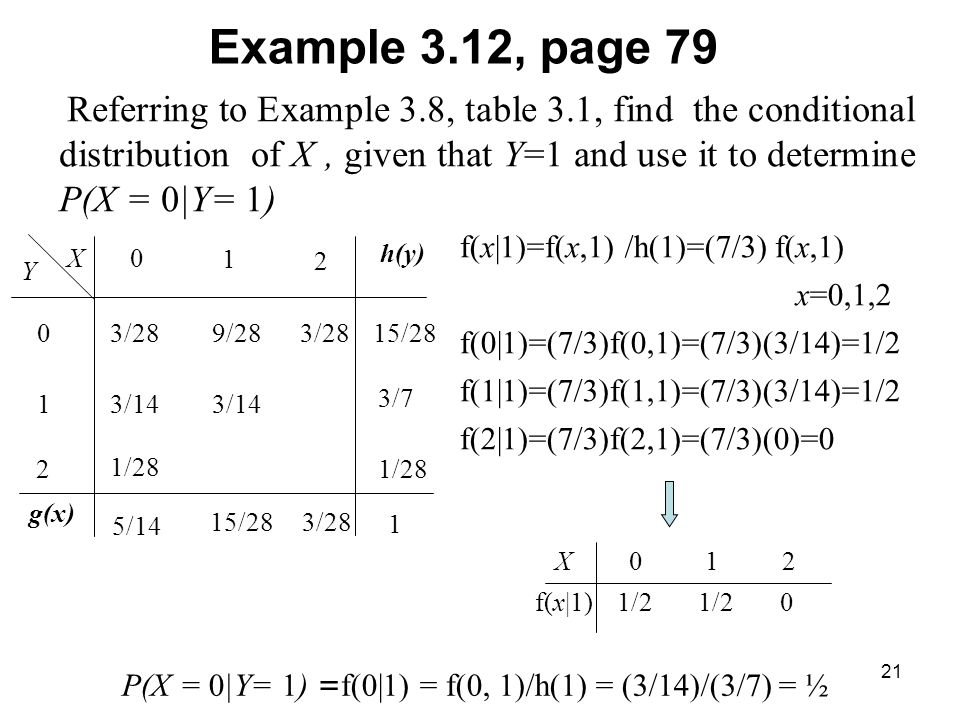


3 4 Joint Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download



The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics



Expected Value Wikipedia


Www Usna Edu Users Oceano Raylee Sm223 Ch12 1 Stewart 16 Pdf


Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch2annotated Pdf



Joint Probability Distribution Wikipedia
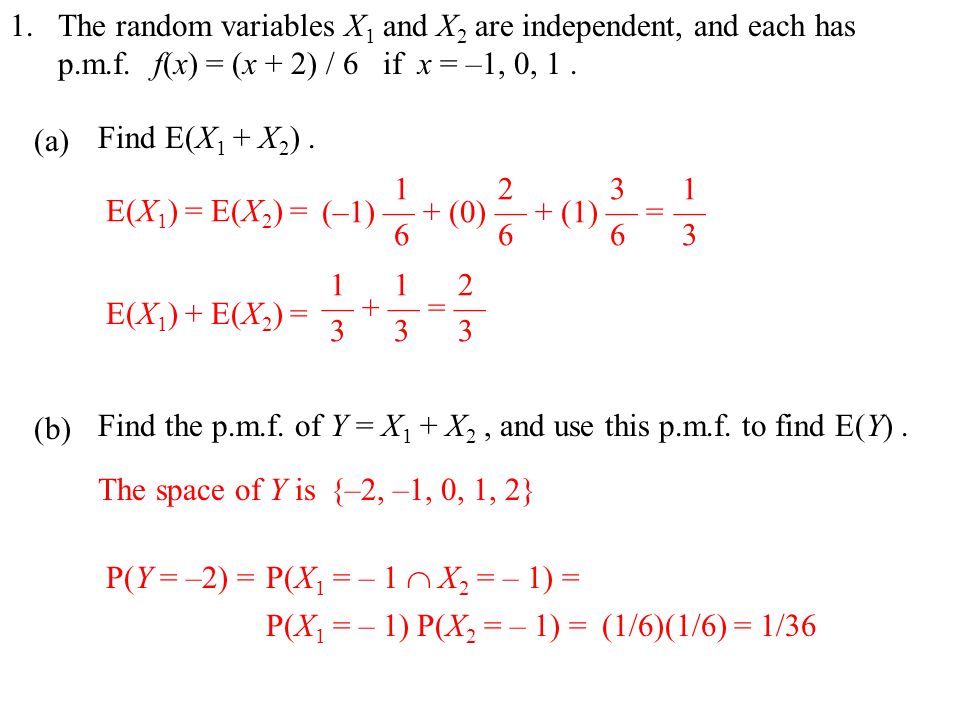


1 A B The Random Variables X 1 And X 2 Are Independent And Each Has P M F F X X 2 6 If X 1 0 1 Find E X 1 X 2 E X 1 E X Ppt Download



Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science



Correlation And Dependence Wikipedia



Is It Appropriate To Use P X X 2 P X X In A Secondary Statistics Textbook In This Content Mathematics Stack Exchange
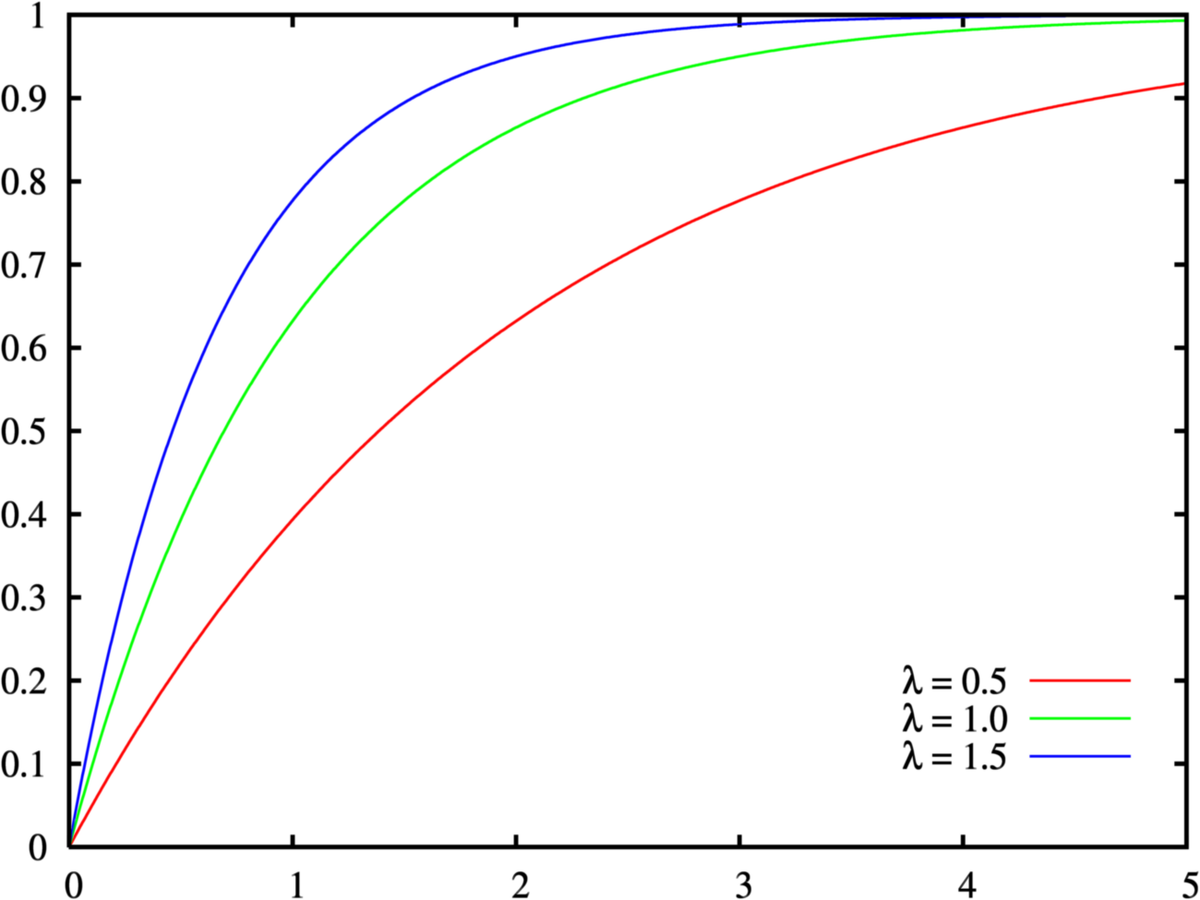


Cumulative Distribution Function Wikipedia



Solved Let The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Chegg Com



Expected Value And Variance Of Discrete Random Variables Youtube
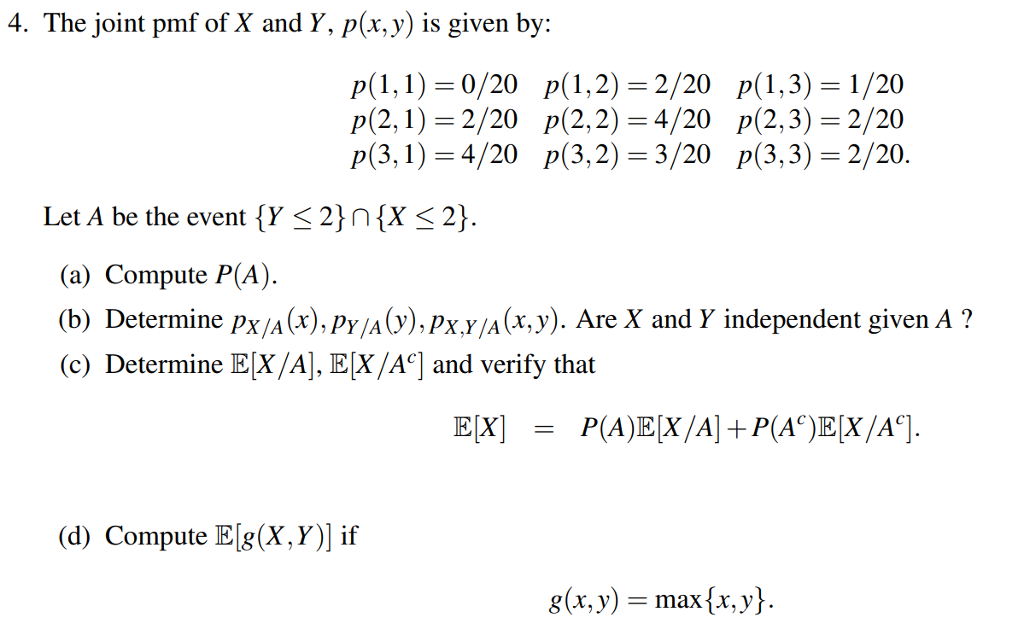


Solved 4 The Joint Pmf Of X And Y P X Y Is Given By Chegg Com
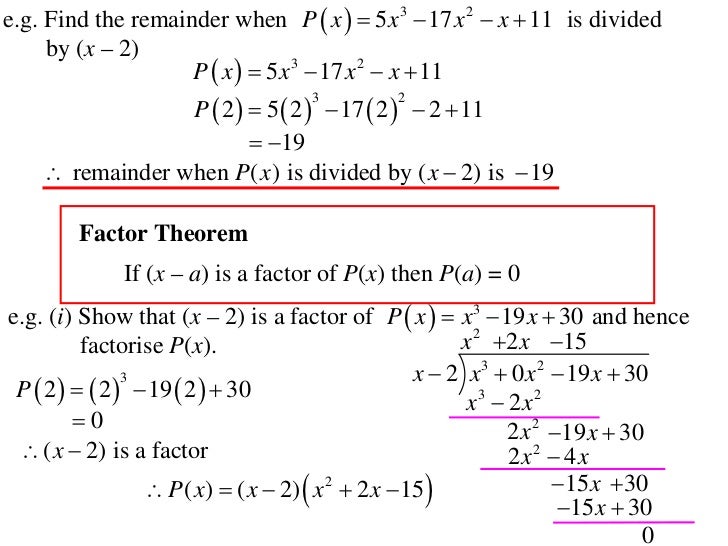


11x1 T15 04 Polynomial Theorems



Ex 2 2 3 Verify Whether Following Are Zeroes Of The Ex 2 2
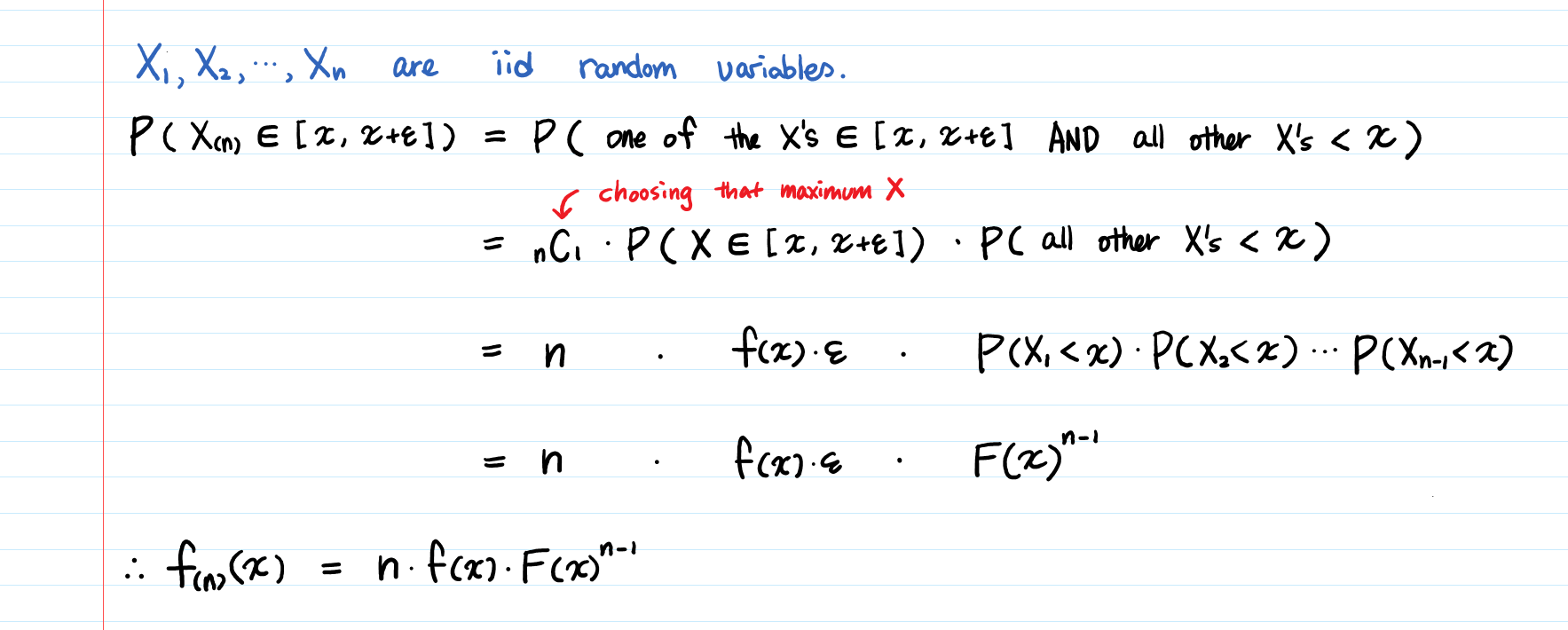


Beta Distribution Intuition Examples And Derivation By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science



Find P X Y Le 0 Given The Joint Probability Function Of X And Y Mathematics Stack Exchange



Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science
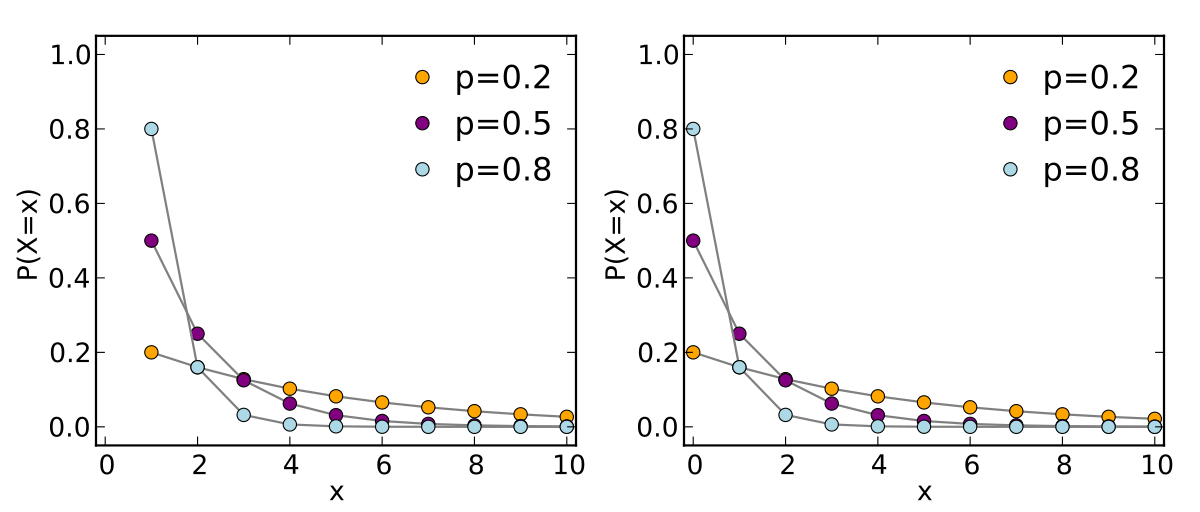


Geometric Distribution Wikipedia



Example 3 Find Zeroes Of Polynomial X2 3 And Verify Examples
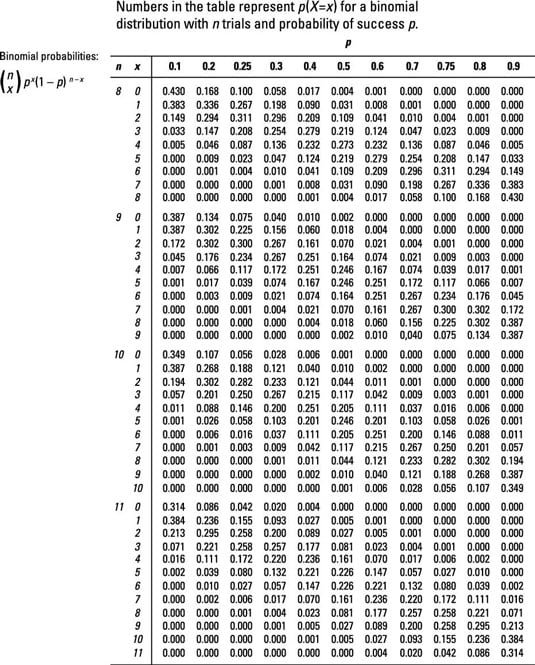


Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies



Ex 2 2 3 Verify Whether Following Are Zeroes Of The Ex 2 2



Solved Suppose That X And Y Have A Joint Pdf F X Y 2 3 Chegg Com


Q Tbn And9gctqsop5xoyrsdnd92znktpup9 Ctr1ohag3khqngrp Ali2fxrt Usqp Cau



Funcion De Probabilidad De La Distribucion Binomial



Example 2 Find The Zeroes Of X2 7x 10 And Verify Examples


Q Tbn And9gcr8eiry5i6fjkrn3asviqugb50j6vhc03jo8tnxwqex4qy3la2z Usqp Cau
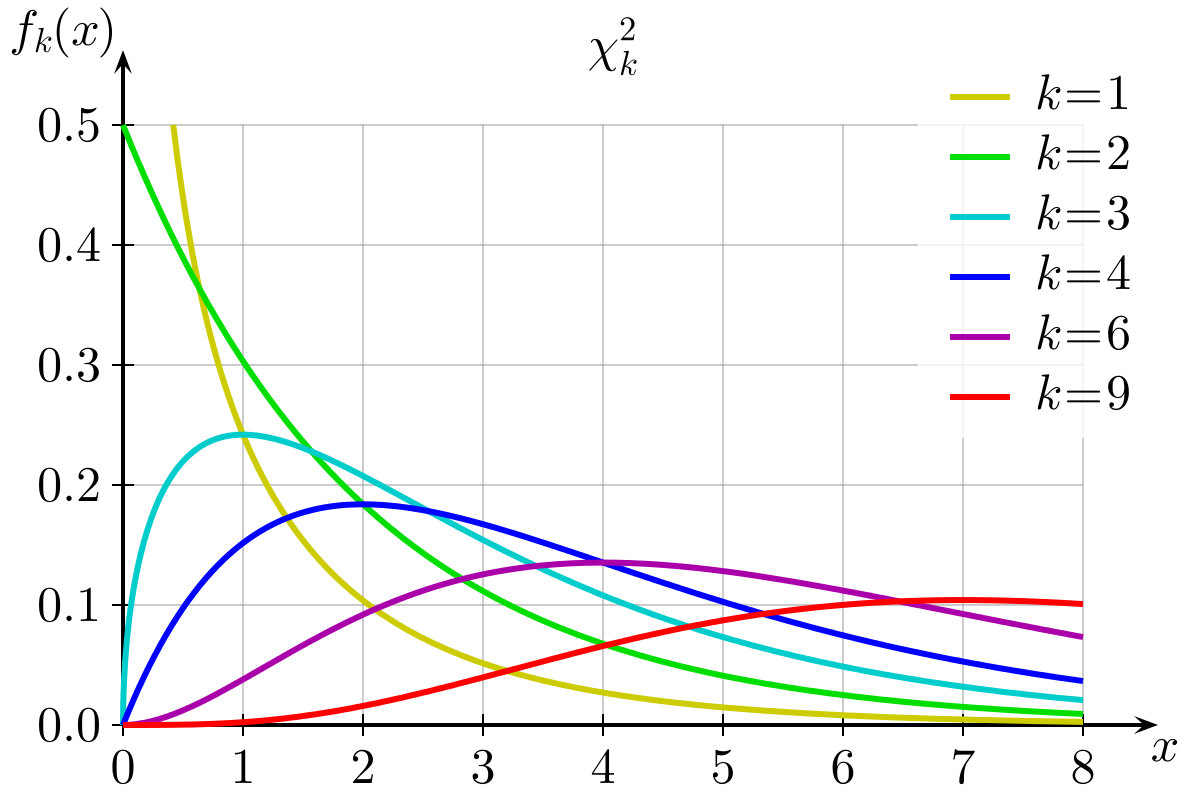


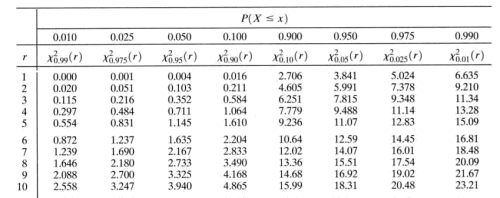
Chi Square Distribution Wikipedia
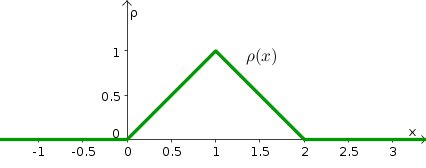


The Idea Of A Probability Density Function Math Insight
/Chi-square_distributionCDF-English-676c564a2ae94aa28670e15aaaf3179c.png)


Degrees Of Freedom Definition


Q Tbn And9gcr25tef6v4nurws2kngeqzdif04iob3esypvergphtjedi 3mll Usqp Cau


コメント
コメントを投稿